Segment builder: attributes & conditions, compound attributes, parentheses, exclusion
|
Learn from this article about:
Attributes and compound attributes, data types and conditions |
HowAttributes toand addcompound attributes, conditions,data movetypes, and deleteavailable themconditions
It is possible to set conditions for each attribute in the segment. They are used to specify attributes and narrow the audience.
Go to the Segment Detail tab (either create a segment or edit an existing one) and click "Add Condition". You can add as many attributes as you wish and specify a condition and/or variousmultiple conditions for each.
AttributesLearn andmore: compoundquick attributes,tutorial dataon types,how andto availablebuild conditions
segments of customers.
Various attributes are inof certain data types.type. In most cases, those are:
- string (attributes like "city" with different cities assigned to each customer)
- numeric (attributes like "number of transactions" with other numbers for each customer)
- date (or datetime) (attributes like "date of birth" with various dates for each customer)
- boolean (attributes like "subscribed to the newsletter" with option yes/ no)
Each of the attributes has certain conditions available basedBased on the typestype mentionedof above.attribute, various conditions are available.
| Conditions available | |
| String attribute |
Equals/ Not equals Equals any of/ Doesn't equal any of Contains/ Not contains Contains any of/ Doesn't contain any of Is known/ Is unknown Remember: string conditions are not listed in alphabetical order, but the most popular values will be listed on the top of the search box instead. Remember: search is case-insensitive. Remember: for string attributes that contain conditions, it should contain at least 3 characters. Remember: it is possible to add multiple values separated by the new line. To do so just select equals any of/ doesn't equal any of/ contains any of/ doesn't contain any of (coming soon). |
| Numeric attribute |
Equals any of/ Doesn't equal any of Lower than (for lower than is equal and lower than defined number) Greater than (for greater than is equal and greater than defined number) Between ( from equal and higher to equal and lower than defined number) Is known/ Is unknown Remember: attributes greater than 0 do not include 0. Remember: it is possible to add multiple values separated by the new line. To do so just select equals any of/ doesn't equal any of/ contains any of/ doesn't contain any of (coming soon). |
| Date (datetime) attribute |
Exactly Since Until Since- until Matches current day Matches current week (coming soon) Matches current month Matches current year Is known/ Is unknown Learn more: about the date (datetime) attribute and how to use them, please refer to this article. |
| Boolean attribute |
Yes/ No |
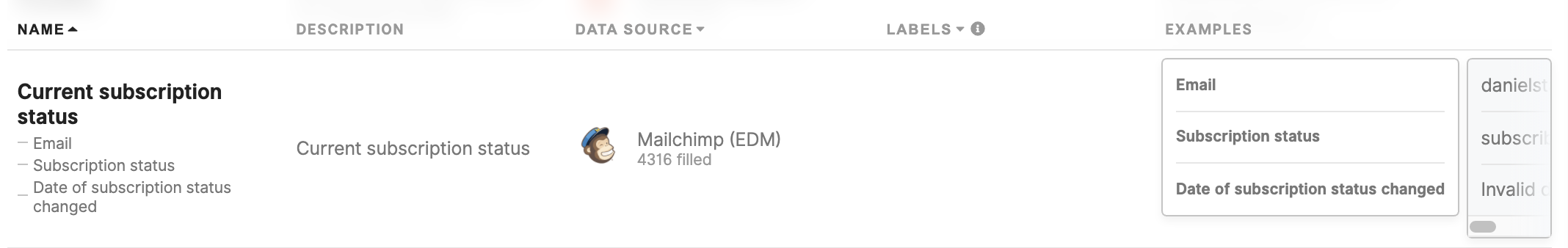
Compound attributes
SomeCompound conditionsattributes have more dimensions that are built from compound attributes (like in the example below for the "Current subscription status" attribute, we have various dimensions available "Email", "subscriptionSubscription status", "Date of subscription status").
Compound attributes work the same as other attributes. They are there to help you see that they belong to the same group of attributes logically put together.
"And"/ "or" operators
In between,between youattributes, can chooseselect the operator "and/ or" to specify the segmentation query further.operator.
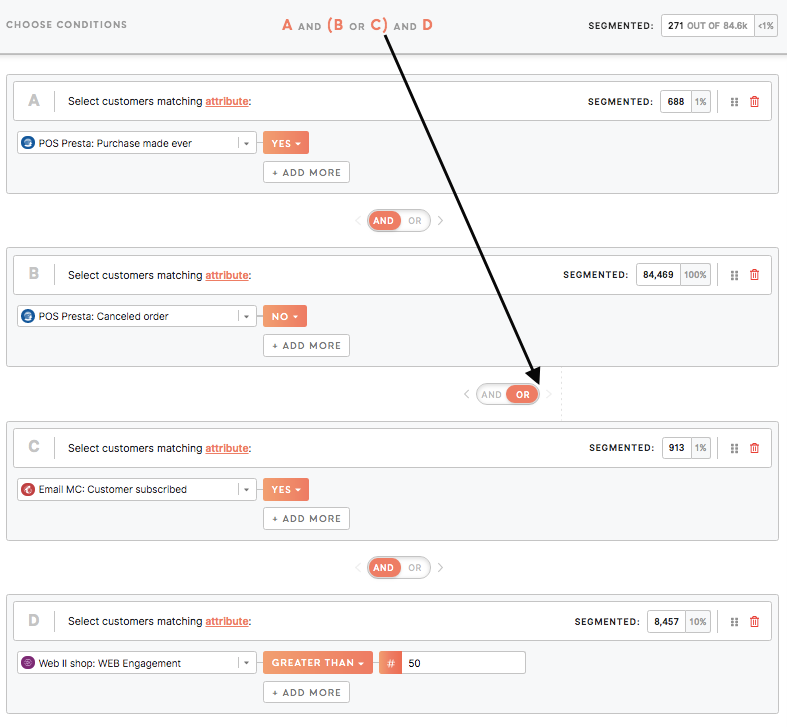
Remember: AND has higher precedence over OR. For example, if defined A and B or C, in fact. it will behave in this way: (A and B) or C.
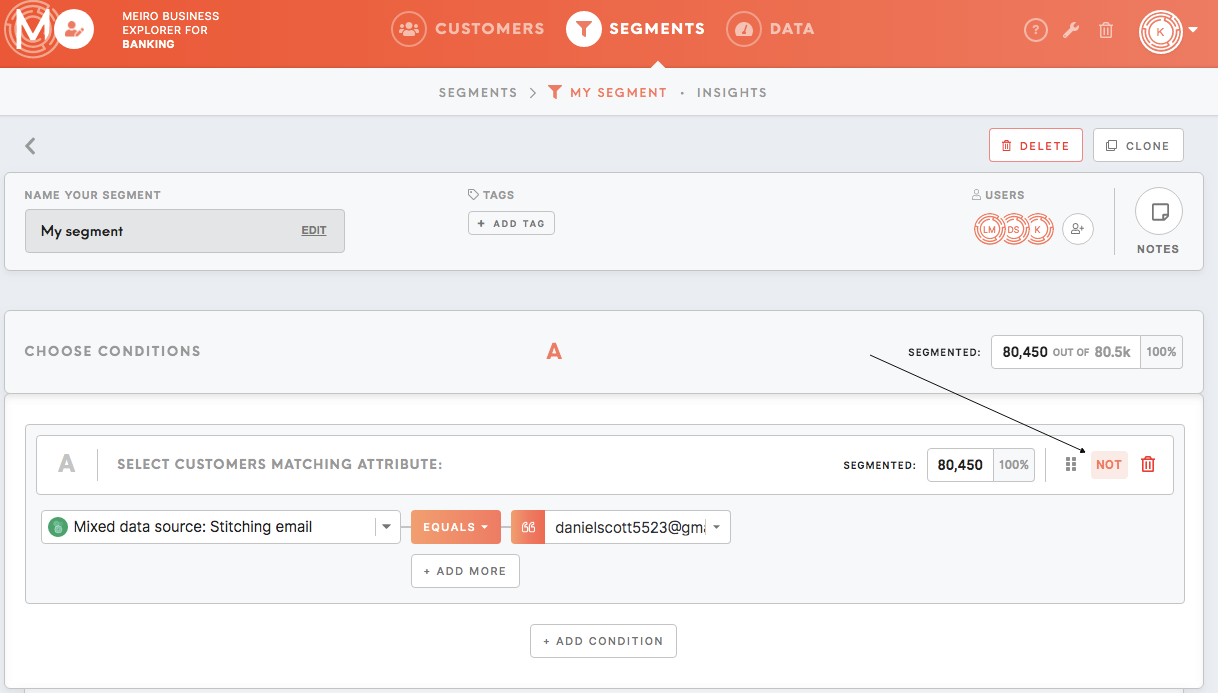
Exclusion
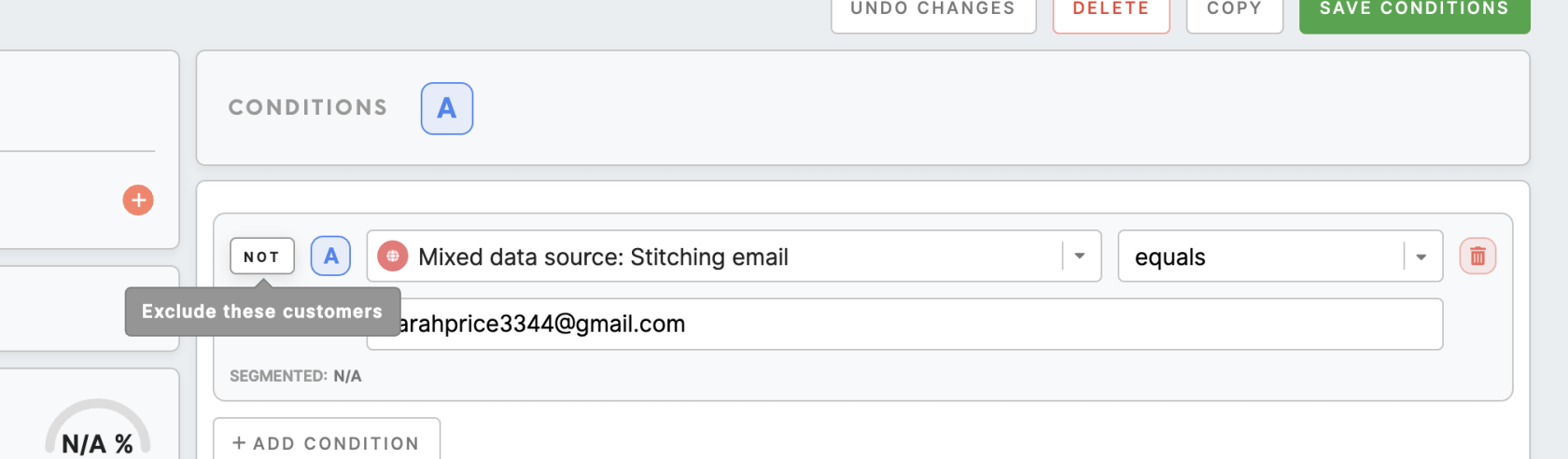
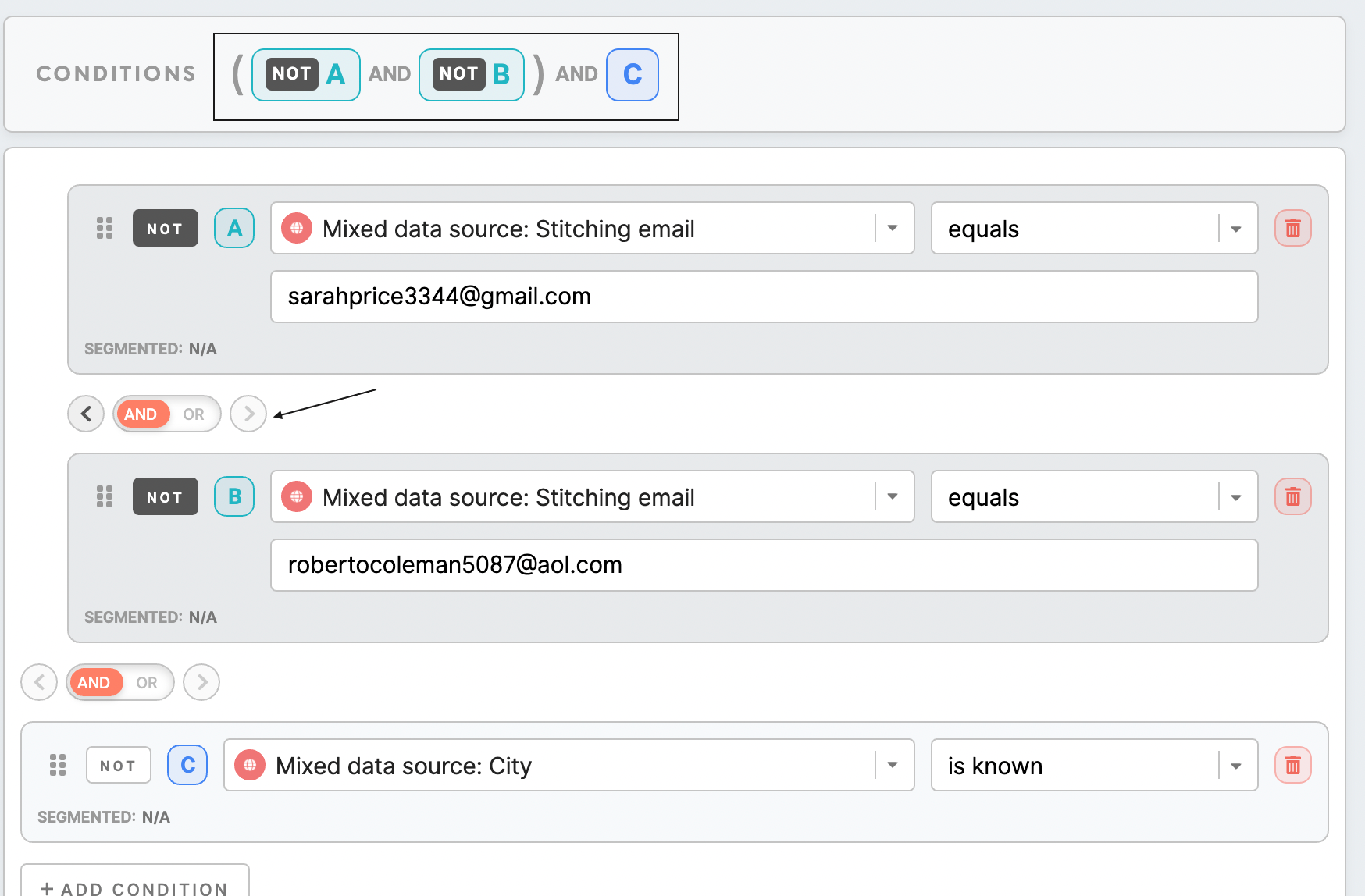
It is possible to set condition negation by clicking on the "Not" button. In this way, it is possible to exclude specific values.
For example, chooseselect all customers who do not equal email denielscott5523@gmail.com, as we wishsarahprice3344@gmail.com to exclude this particular customer.email from your search.
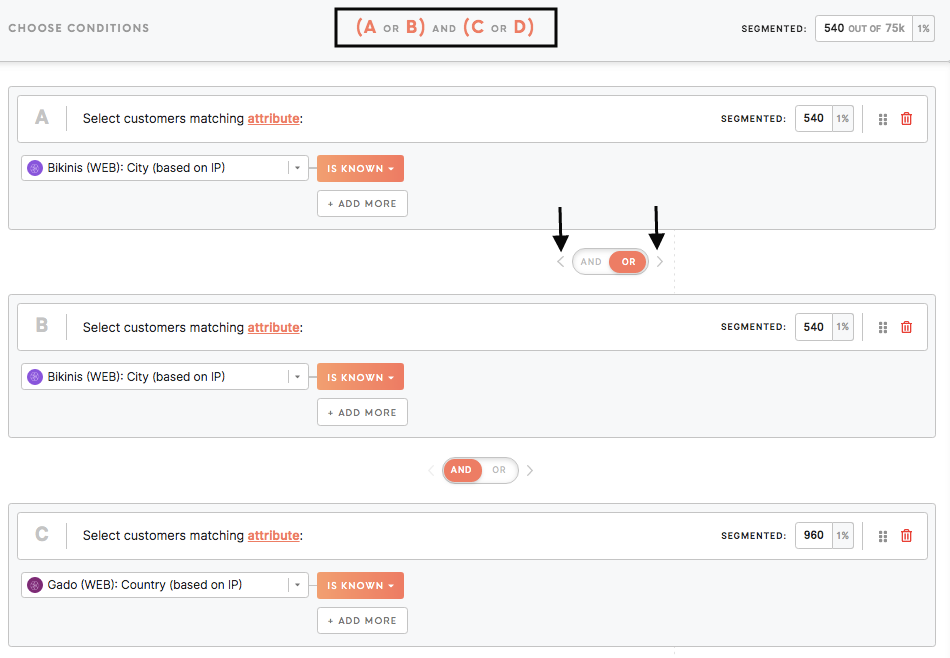
Parentheses
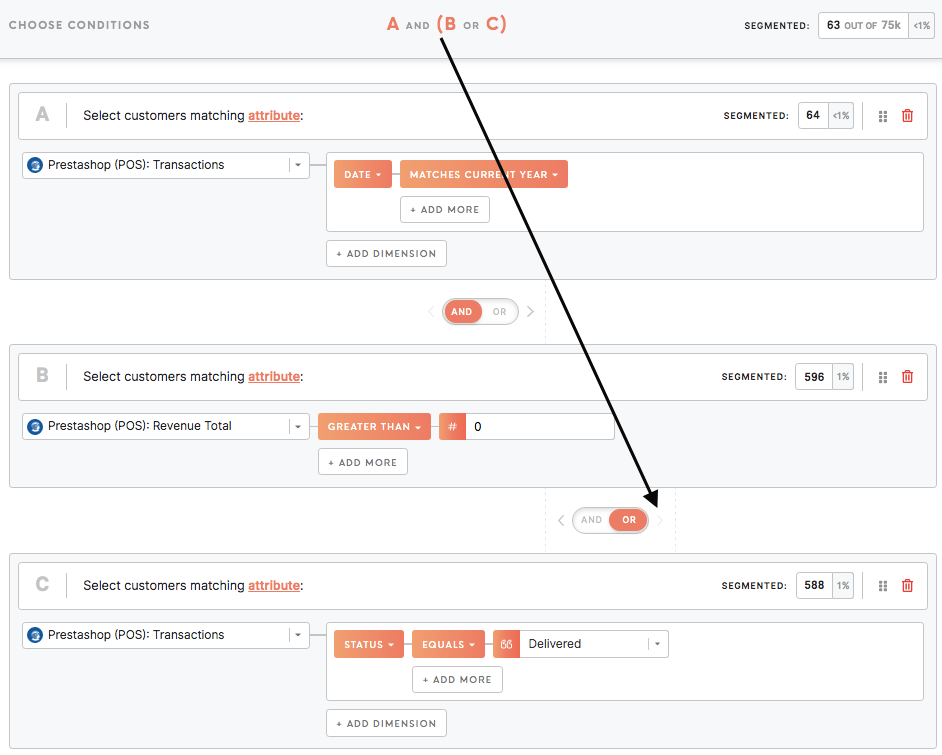
Set parentheses () to specify the query. For example, "(A or B) and (C or D)": customers from "(A Jakarta or B Singapore) and (C subscribed to an email or D made a transaction)".
Remember: AND has higher precedence over OR. For example, if defined A and B or C, in fact, it will behave in this way: (A and B) or C.
|
Example 1: Customers -have ever made a and -highly engaged on the website that canceled orders or subscribed to an email |
|
|
Example 2: Segment customers -have made a transaction in the current year and -spent more than 0 or -have ever made a transaction with status |
|
Tutorials
Customers who have email engagement in a particular country
Customers who visited the website, added items to the cart but left without a purchase
Engaged customers who prefer browsing on a mobile device
Website visitors who are non-customers